Innovation rarely arrives fully formed—it grows out of countless trials, errors, and the courage to explore untested paths. At the center of this transformative process lies experimentation, a practice that allows individuals, companies, and even entire industries to learn, adapt, and ultimately thrive. When approached strategically, experimentation becomes more than a method of testing ideas; it becomes the foundation of long-term growth, resilience, and breakthrough success.
The Essence of Experimentation
Experimentation is not just about testing theories in a lab or conducting rigid scientific trials. It’s about adopting a mindset that welcomes uncertainty and embraces discovery. Every new product, business model, or social shift is built on someone’s willingness to ask, “What if we tried this?”
When Thomas Edison famously tested thousands of filament options before inventing a practical light bulb, his work embodied experimentation at its core. He didn’t see failure as wasted effort—he saw it as data. This attitude underpins innovation across every discipline, from medicine and technology to marketing and design.
Why Experimentation Drives Innovation
The link between experimentation and innovation is undeniable. Without testing, iteration, and refinement, bold ideas remain abstract. Experimentation bridges the gap between imagination and reality. Here’s why it matters so profoundly:
- It reduces the risk of costly mistakes by validating assumptions early.
- It reveals unexpected insights that challenge conventional wisdom.
- It encourages agility, allowing businesses to adapt faster than competitors.
- It builds resilience by normalizing failure as part of progress.
A study published by Harvard Business Review highlighted that organizations with strong cultures of experimentation consistently outperform peers, particularly in fast-changing industries. When leaders allow teams to test and learn without fear, they unlock creativity that rigid systems suppress.
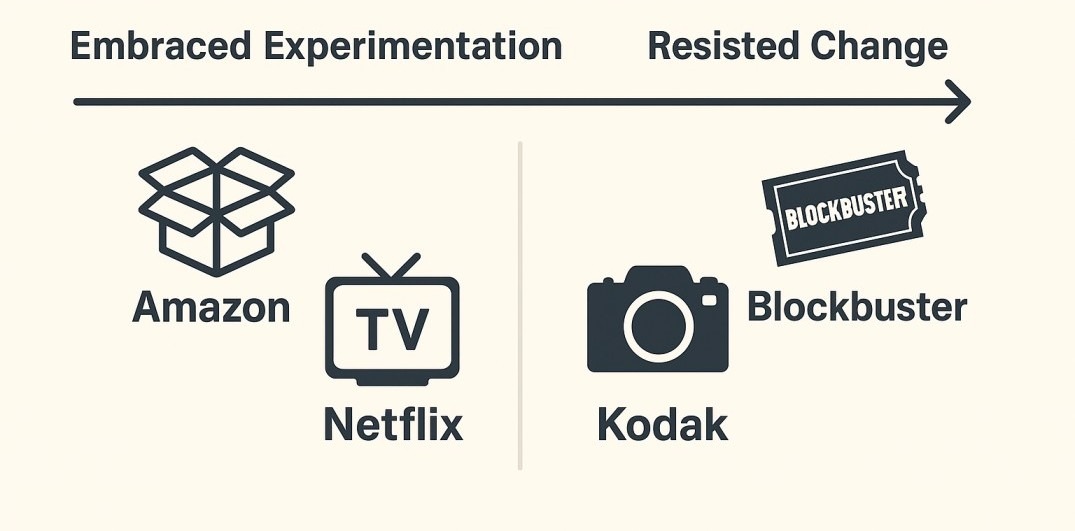
Experimentation in Business: From Startups to Giants
Businesses across all sectors rely on experimentation to remain competitive. Startups, constrained by resources but fueled by ambition, thrive by continuously testing ideas in lean and flexible ways. The concept of the “Minimum Viable Product” (MVP) is itself rooted in experimentation—it allows entrepreneurs to introduce stripped-down versions of their ideas, collect feedback, and iterate rapidly.
At the other end of the spectrum, global corporations also depend on experimentation. Amazon runs thousands of controlled experiments annually, tweaking everything from checkout flows to product recommendations. Netflix, similarly, refines its algorithms through rigorous testing to ensure viewers remain engaged. Both companies credit their success not to a single stroke of genius, but to continuous, structured experimentation.

The Role of Experimentation in Science and Technology
While business provides clear examples, the roots of experimentation lie in science. The scientific method—hypothesis, test, observation, conclusion—is a structured form of experimentation that has propelled humanity forward for centuries. Breakthroughs in medicine, climate research, and artificial intelligence exist because researchers were willing to push boundaries and verify results under controlled conditions.
In technology, experimentation accelerates progress at lightning speed. Developers run A/B tests to optimize digital products, while researchers explore neural networks by testing countless iterations of algorithms. Without these ongoing experiments, progress in fields like machine learning or biotechnology would stall.
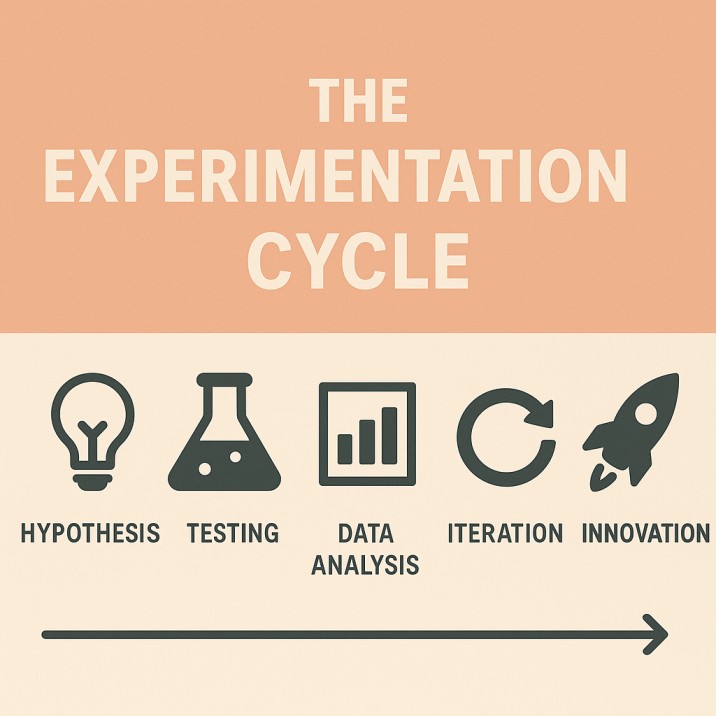
Overcoming the Fear of Failure
The greatest barrier to experimentation is fear. Many individuals and organizations hesitate to test new ideas because they associate failed outcomes with wasted effort. Yet, the most innovative companies flip this mindset: they view failure as essential data.
Psychologists emphasize that experimentation builds resilience. By reframing mistakes as valuable learning moments, people become more open to risk-taking. This is why companies like Google encourage “psychological safety”—a culture where employees know they can try, fail, and still have their ideas respected.
For individuals, adopting an experimentation mindset means testing career choices, side projects, or new learning strategies without obsessing over perfection. By leaning into curiosity instead of fear, breakthroughs often emerge unexpectedly.
Experimentation in Marketing and Consumer Behavior
Modern marketing thrives on experimentation. Digital platforms allow businesses to test campaigns in real time, with measurable results. Whether adjusting ad copy, exploring influencer partnerships, or tailoring offers through personalization, marketers succeed when they run experiments continuously.
For example, A/B testing—a cornerstone of digital marketing—relies entirely on experimentation. Marketers test two versions of a webpage or ad, analyze user responses, and refine based on evidence. This approach has transformed guesswork into a science of optimization.
Experimentation as a Growth Mindset
Beyond business and science, experimentation can serve as a personal growth strategy. Trying new hobbies, testing productivity systems, or experimenting with fitness routines allows individuals to discover what works best for them.
The key is embracing iteration: small steps, reflective learning, and gradual refinement. As with businesses, personal success is rarely a single leap forward—it’s a series of experiments, each revealing a clearer path.
The Future Belongs to Experimenters
In a world defined by rapid change, those who rely solely on tradition risk being left behind. The pace of technological evolution, climate adaptation, and shifting cultural dynamics demands bold experimentation. From climate scientists testing sustainable solutions to entrepreneurs rethinking work-life balance, experimentation is no longer optional—it’s the engine of survival.
Conclusion
Experimentation is more than trial and error—it’s a disciplined yet open-minded approach to discovery. Innovation doesn’t happen in a straight line; it emerges from curiosity, risk-taking, and a willingness to learn from every outcome.
For businesses, embracing experimentation can mean the difference between growth and irrelevance. For individuals, it can open doors to self-discovery and resilience. For society at large, it holds the key to solving humanity’s greatest challenges.
Ultimately, experimentation is the bridge between imagination and reality—the key to innovation and breakthrough success.
Andrea Balint is a writer and researcher focused on human behavior, workplace psychology, and personal growth. Through her work at CareersMomentum, she explores how mindset, leadership, and emotional intelligence shape modern careers. With a background in communication and HR development, she transforms complex ideas into practical insights that help readers build clarity, confidence, and professional purpose.
