The term communication skills definition may sound like something abstract you only encounter in textbooks, yet it shapes everything from how you lead a meeting to how you comfort a friend. Communication is not just about talking or writing; it is the invisible architecture of connection. When you understand what communication skills truly mean, you unlock the ability to influence, align, and empathize with precision.
At its core, the communication skills definition revolves around the exchange of meaning. It includes how thoughts move from one mind to another, how tone frames perception, and how silence itself can speak louder than words. A person with strong communication skills doesn’t simply transmit information—they ensure understanding occurs.
The communication skills definition explains how meaning moves from one mind to another with clarity, empathy, and intent. It involves aligning thought, tone, and perception to create true understanding rather than mere expression. Strong communication skills connect emotion with logic, turning dialogue into influence and collaboration. Mastering this definition strengthens relationships, leadership, and the ability to inspire action through precise and compassionate expression.
The Essence of the Communication Skills Definition
When people first encounter the communication skills definition, they often think of speaking clearly or writing correctly. But clarity is only one part. The deeper meaning lies in synchronization—how your intent and your message align with the receiver’s interpretation. Communication, then, becomes an act of design: you are constantly engineering the bridge between idea and understanding.
Language, emotion, and context intertwine to shape the quality of that bridge. The communication skills definition is incomplete without mentioning emotional intelligence. Knowing when to pause, when to clarify, and when to simplify makes the difference between a message that lands and one that vanishes.
Communication Skills Definition Through the Lens of Behavior
While definitions often remain conceptual, the behavioral layer of communication is what makes theory real. The communication skills definition expands when you observe how gestures, eye contact, tone, and even digital cues contribute to meaning. A simple thumbs-up emoji in a chat thread might be affirmation or dismissal, depending on context.
Human behavior in communication follows patterns. The more awareness you bring to your habits, the stronger your skill becomes. The communication skills definition embraces adaptability—the ability to shift tone or method based on audience, goal, and medium. For example, empathy-driven responses create trust in customer service, while concise instructions drive efficiency in management.
The Cognitive Dimension of the Communication Skills Definition
Cognitive processes are the hidden machinery behind communication. When someone listens, they decode, analyze, and reconstruct meaning in milliseconds. Understanding that this process varies between individuals brings compassion to every exchange.
The communication skills definition therefore includes mental clarity—your ability to structure thoughts before expression. Many breakdowns occur not because of vocabulary but because of disorganized thinking. A strong communicator simplifies complexity, guiding others through logic without drowning them in jargon.
In a world overloaded with information, attention becomes the new currency. The sharper your communication, the longer you hold it. The communication skills definition must now encompass cognitive empathy—the discipline of seeing how others think before deciding what to say.
Emotional Resonance: The Heart of Connection
If clarity defines the head of communication, emotion defines its heart. The communication skills definition grows incomplete without emotional resonance. People remember how you make them feel far longer than the details of what you said.
Emotionally intelligent communication blends empathy with precision. It’s the awareness that words can heal, provoke, or inspire depending on tone and timing. The communication skills definition here expands into relational trust—your ability to create safety for others to express themselves without judgment.
Empathy transforms communication from transaction to transformation. When you acknowledge others’ experiences, you reduce defensiveness and open the door to genuine dialogue.
Digital Communication and Modern Redefinition
In the digital age, the communication skills definition has evolved dramatically. Tone now travels through text, and misunderstandings multiply without facial or vocal cues. The ability to communicate effectively online is no longer optional—it defines credibility and professionalism.
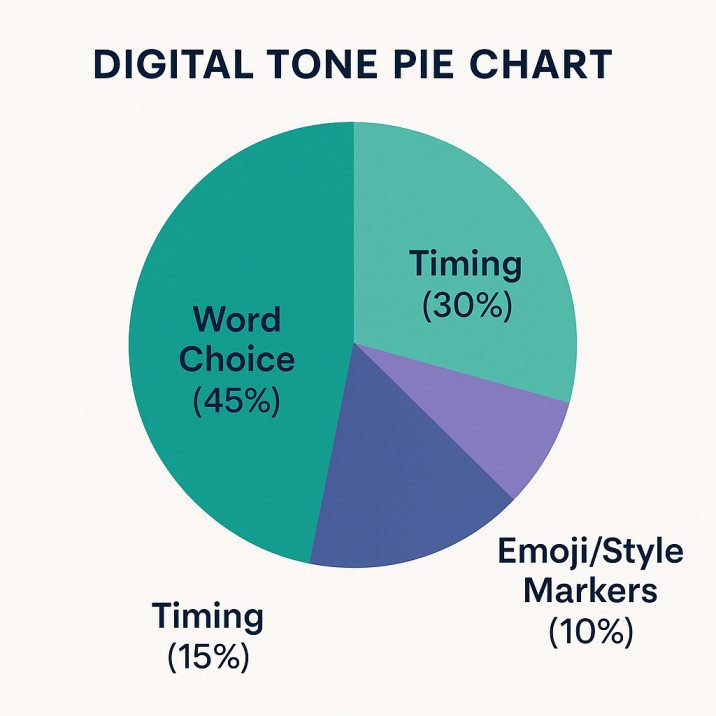
Digital communication skills require balance between brevity and nuance. Every emoji, punctuation mark, or delay carries subtext. The modern communication skills definition incorporates media literacy—knowing which channel fits which message. A formal email differs from a Slack chat not just in tone but in implied authority.
Online, clarity becomes empathy. When you write as if the reader cannot ask follow-up questions, your message becomes self-sufficient, efficient, and respectful.
The Leadership Connection
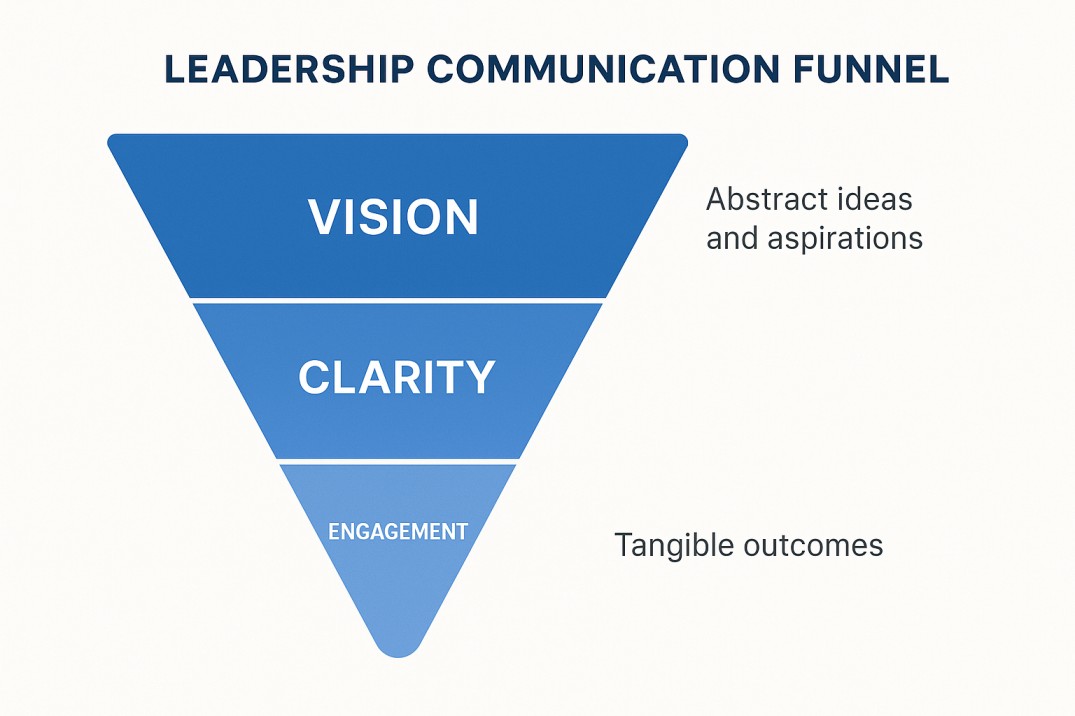
The communication skills definition in leadership settings focuses on influence through clarity and trust. A leader doesn’t just disseminate information—they translate vision into collective motivation. Words, tone, and timing can turn a team from compliant to committed.
Leaders with refined communication skills listen as much as they speak. Listening signals respect, which amplifies authority. Within the communication skills definition, feedback loops become the backbone of organizational alignment. By inviting dialogue instead of dictation, leaders gain engagement instead of resistance.
Communication here is strategy. It turns abstract goals into executable actions, transforming culture itself.
Communication Skills Definition and Self-Awareness
The most overlooked aspect of the communication skills definition is self-awareness. Every message you send reflects your perception of yourself and others. People who communicate well manage both what they express and how they react.
Self-awareness involves recognizing emotional triggers, biases, and tendencies. Some speak too quickly out of anxiety; others withhold due to fear of conflict. Refining communication means refining the self. The communication skills definition becomes not just an interpersonal tool but a mirror of maturity.
When you become aware of your impact, communication shifts from accidental to intentional. Words turn from reflex to craft.
Measuring Communication Skills
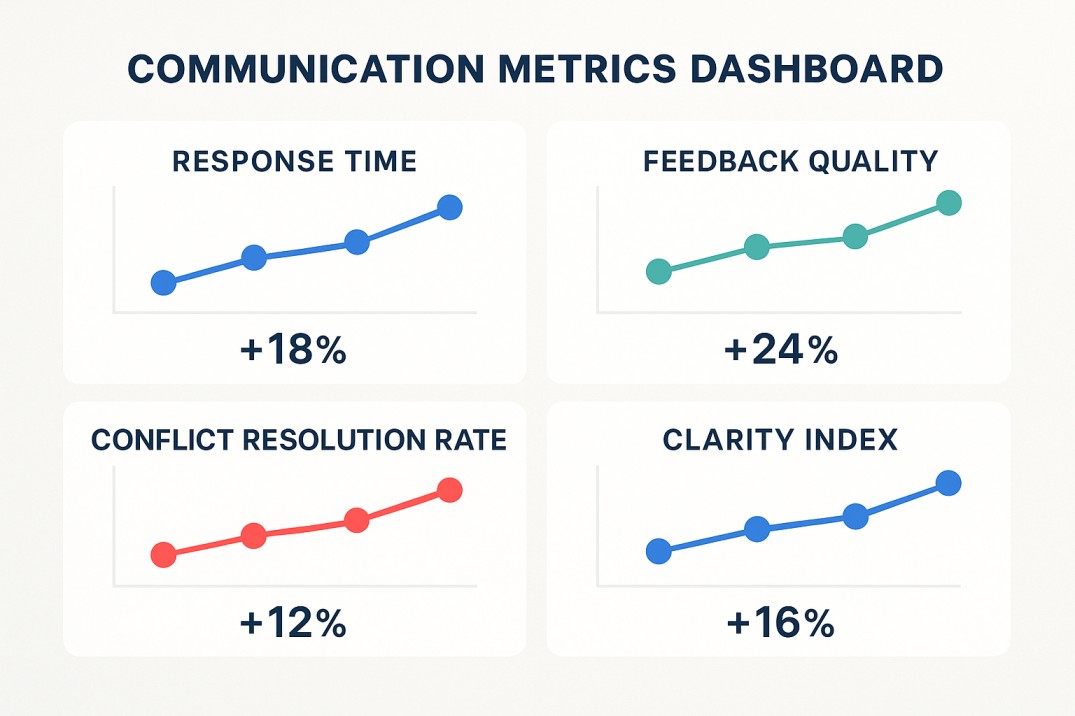
Though the communication skills definition seems qualitative, it can be measured through outcomes: trust built, conflicts resolved, ideas executed. Organizations often evaluate communication effectiveness using engagement surveys, performance reviews, and peer feedback.
Metrics help you turn subjective impressions into data. Tracking how well information flows between teams or how often clarifications are needed shows where to improve. The communication skills definition thus merges art and analytics.
The key is consistency. Measurement without follow-up only records problems; applying insights transforms them.
The Framework You Can Use
After examining layers of the communication skills definition, a practical framework emerges—one that integrates clarity, empathy, adaptability, and reflection.
- Clarity gives structure to thought.
- Empathy bridges emotional distance.
- Adaptability ensures relevance across channels.
- Reflection turns every conversation into learning.
Though we avoid list-style writing, these dimensions blend seamlessly. They are not steps to follow but muscles to strengthen simultaneously. Together, they redefine the communication skills definition as a living framework rather than a fixed rulebook.
Mastering communication is an ongoing cycle—observe, express, listen, adjust, repeat. Each interaction refines your next.
The Broader Meaning of the Communication Skills Definition
In truth, the communication skills definition is far more than the sum of words and gestures. It is the foundation of relationships, leadership, education, and innovation. No technology can replace the human art of connection.
Every breakthrough—scientific, emotional, or organizational—begins with someone communicating an idea clearly enough for another to act on it. The communication skills definition thus becomes a human constant: the bridge between thought and progress.
Understanding and applying this framework turns communication from an instinct into an advantage. The ability to be understood—and to understand others—remains one of the rare skills that never loses value.
Andrea Balint is a writer and researcher focused on human behavior, workplace psychology, and personal growth. Through her work at CareersMomentum, she explores how mindset, leadership, and emotional intelligence shape modern careers. With a background in communication and HR development, she transforms complex ideas into practical insights that help readers build clarity, confidence, and professional purpose.
