In the demanding crucible of leadership, the age-old debate of accountability vs responsibility continues to simmer. While both are undeniably crucial ingredients for forging a successful team and achieving desired outcomes, a crucial distinction lies beneath the surface. Understanding this difference is the key to fostering a thriving environment where individuals are empowered to excel.
This article delves into the nuanced differences between accountability and responsibility. We’ll explore how responsibility establishes the foundation – the defined roles and tasks that each team member contributes. Accountability, however, goes a step further. It’s about taking ownership of the results, for better or worse. We’ll illustrate this distinction with real-world scenarios and explore the significant benefits a culture of accountability vs responsibility unlocks for both leaders and teams. Finally, we’ll equip leaders with a roadmap to cultivate a thriving environment built on shared ownership and a relentless pursuit of excellence.
Understanding Leadership Identity
Leadership is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various qualities, skills, and behaviors necessary to guide, inspire, and influence individuals or groups toward a common goal or vision.
Authoritarian Leadership
Characterized by centralized decision-making, stringent control, and a delineated hierarchy, authoritarian leadership is particularly effective in crisis management scenarios demanding prompt decisions. Leaders adopting this style must judiciously balance authority with the preservation of team morale and engagement.
Transformational Leadership
Transformational leaders inspire and motivate teams, fostering innovation and personal and professional growth. This style proves particularly efficacious in spearheading change initiatives and cultivating high-performing teams. Leaders embracing this approach prioritize relationship-building, instill a sense of purpose, and contribute to the development of a positive organizational culture.
Servant Leadership
At the core of servant leadership lies a commitment to serving others, characterized by empathy, collaboration, and a focus on team members’ well-being. This style is instrumental in team building and establishing a positive organizational culture. Servant leaders prioritize the needs of their team, aiming to empower and support individual growth for the collective success of the organization.
Democratic Leadership
Democratic leaders advocate for inclusive decision-making, involving team members in the process and fostering open communication. This approach is apt for collaborative projects and creative brainstorming sessions, leveraging diverse perspectives within the team. While potentially time-consuming, the benefits of heightened engagement and commitment often outweigh the associated challenges.
Laissez-Faire Leadership
Laissez-faire leaders embrace a hands-off approach, entrusting team members with tasks and relying on their capabilities. This style is most effective when leading self-motivated and skilled teams. However, a judicious equilibrium must be maintained to prevent delegation from devolving into a lack of direction or accountability within the team.
Visionary Leadership: Setting the Milestone
One of the most critical roles of a leader is to define what the milestone is and why it matters. A leader must be able to articulate a clear and compelling vision of the goal. This vision acts as the north star for the team, guiding all efforts and decision-making. Without a clear vision, teams may find it difficult to stay focused or aligned.
For example, if a team is working on a new product launch, the leader must define what “success” looks like for that launch. Is it reaching a certain number of sales in the first month? Is it gaining market share or improving customer satisfaction? By clearly setting the milestone, the leader helps the team understand the desired outcome and how they can contribute to achieving it.
Emotional Intelligence Habits and Examples Explained
Emotional intelligence (EI) involves the ability to understand and manage your emotions, as well as recognize and influence the emotions of others. Cultivating habits that enhance emotional intelligence can lead to better relationships, improved leadership skills, and greater personal and professional success. Here are some key emotional intelligence habits, accompanied by examples:
- Self-awareness
Habit: Regularly reflecting on your emotions.
Example: Keeping a journal to explore your feelings after significant events or interactions, helping you understand your emotional responses and triggers.
- Self-regulation
Habit: Practicing mindfulness and stress-reduction techniques.
Example: Using deep breathing or meditation to calm down before responding in a stressful situation, allowing you to react more thoughtfully.
- Motivation
Habit: Setting personal and professional goals that are aligned with your values.
Example: Creating a vision board or setting SMART goals to stay focused on what truly motivates you, such as career advancement or personal development.
- Empathy
Habit: Actively listening and showing genuine interest in others’ feelings.
Example: When a colleague is upset, instead of offering quick advice, asking open-ended questions to understand their perspective and feelings fully.
- Social Skills
Habit: Building and maintaining healthy relationships through effective communication.
Example: Regularly checking in with friends and colleagues, acknowledging their achievements, and offering support during challenging times.
- Adaptability
Habit: Being open to change and new ideas.
Example: When a project doesn’t go as planned, instead of resisting feedback, asking for input from team members to find innovative solutions.
- Conflict Resolution
Habit: Approaching disagreements with the intent to understand and find common ground.
Example: During a disagreement with a partner, focusing on understanding their point of view and reaching a compromise that respects both parties’ needs.
- Positive Outlook
Habit: Practicing gratitude and looking for the positive in every situation.
Example: At the end of each day, writing down three things you are grateful for, which can help shift focus from negative to positive aspects of life.
Developing these emotional intelligence habits takes time and conscious effort, but the benefits are profound. By integrating these practices into your daily life, you can enhance your emotional intelligence, leading to more meaningful interactions, improved decision-making, and increased overall well-being.
Responsibility: The Building Blocks of Performance
Let’s begin by laying the foundation. Responsibility refers to the specific duties, tasks, or obligations assigned to an individual or team. It’s akin to being in charge of a particular area or function within the larger organizational machinery. Imagine responsibility as the building blocks – the well-defined roles and tasks that each member contributes to the overall success. For example, a marketing manager holds the responsibility for developing compelling marketing campaigns, a software developer tackles the responsibility of coding specific features, and so on. Effectively fulfilling these responsibilities ensures the smooth operation of the overall system.
Accountability: Owning the Outcome, Not Just the Task
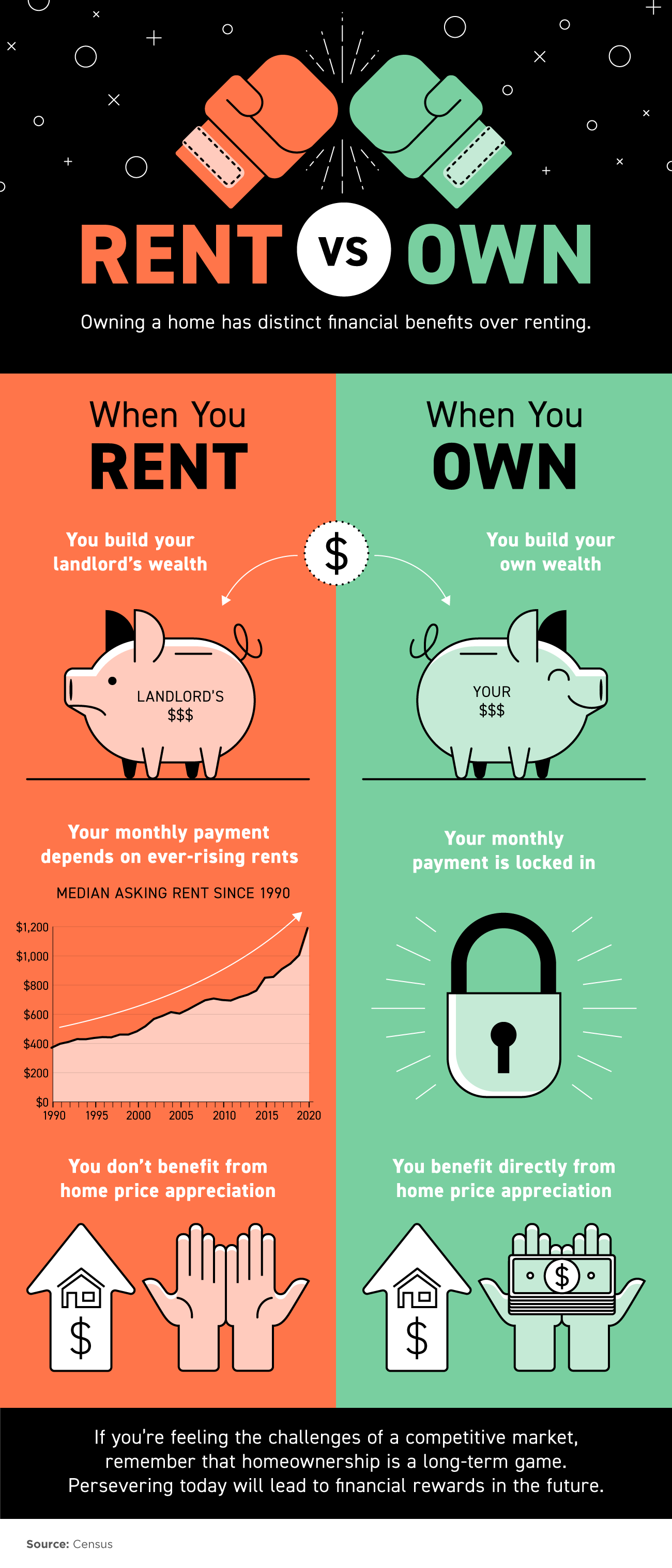
Accountability, however, transcends the mere completion of tasks. It delves deeper, requiring ownership of the results stemming from those tasks – both positive and negative. It’s the unwavering willingness to answer for the success or failure of a project, a critical decision, or even the actions of your team. Effective leaders cultivate a culture of accountability, where every individual grasps their role in achieving the desired outcome and readily accepts being measured on their contribution.
Illustrating the Difference in Action
To solidify this distinction, let’s explore a common scenario: a missed project deadline.
Responsibility
In this instance, the team member assigned to the task acknowledges the missed deadline and explains the reason behind it. They take ownership of the missed task.
Accountability
Here, the team member goes beyond simply acknowledging the missed deadline. They actively propose solutions to mitigate the impact, catch up on the schedule, and implement measures to prevent similar occurrences in the future. They take ownership of the outcome.
Why Accountability Takes Center Stage
While responsibility lays the groundwork, accountability serves as the driving force behind achieving goals. Leaders who prioritize accountability beyond mere task allocation unlock a treasure trove of benefits:
Empowering Ownership
When team members feel accountable, they become more invested in the project’s success. This heightened sense of ownership leads to proactive problem-solving and a drive to excel beyond expectations.
Elevating Performance
The prospect of being held accountable for less-than-stellar outcomes can serve as a powerful motivator. It encourages team members to be more dedicated, meticulous in their work, and strive for excellence in everything they do.
Fostering a Learning Environment
Taking responsibility for both successes and failures fosters a dynamic learning environment. Accountability encourages introspection and analysis of what went right and wrong, leading to continuous improvement and a commitment to learning from mistakes.
Building Stronger Teams
When accountability is a shared responsibility, individuals hold each other and themselves to a higher standard. This fosters collaboration, trust, and a sense of collective responsibility for achieving shared goals.
The Leader’s Guide to Cultivating Accountability
Creating a culture of accountability is not an overnight feat. Here are some effective strategies leaders can employ:
Leading by Example
Actions truly speak louder than words. Leaders set the tone for the organization. By demonstrating unwavering accountability for their own actions and decisions, leaders model the behavior they expect from others.
Crystal Clear Expectations
Clearly defining goals and expectations for every team member and project is paramount. Ensure everyone understands their roles and how their work contributes to the bigger picture.
Empowerment
Invest trust in your team by providing them with the resources and authority necessary to fulfill their responsibilities. This demonstrates trust and fosters a strong sense of ownership.
Open Communication is Key
Encourage open communication and a free flow of feedback. Create an environment where team members feel comfortable discussing challenges, roadblocks, and proposing solutions without fear of retribution. Recognizing and openly discussing both successes and failures is crucial for fostering a culture of accountability.
Recognition and Feedback
Celebrate both individual and team achievements. This fosters a sense of accomplishment and motivates continued excellence. Equally important is providing constructive feedback and coaching opportunities for improvement when necessary.
Focus on Solutions
When challenges arise, shift the focus from assigning blame to collaboratively seeking solutions. Encourage your team to analyze the situation, learn from mistakes, and develop clear plans to move forward productively.
Accountability vs. Micromanagement: Navigating the Divide
It’s crucial to distinguish accountability from the pitfall of micromanagement. Leaders who nurture a culture of accountability trust their team members’ expertise and capabilities. They empower them to make decisions, take initiative, and learn from their experiences. Accountability focuses on the outcome, not the process itself. Conversely, micromanagement involves excessive control and hovering over every detail, leading to stifled creativity, resentment, and a stifled sense of ownership.
The Power of Shared Responsibility

Leaders who create a culture of accountability cultivate a sense of shared responsibility. This fosters a collaborative environment where team members support each other, readily offer assistance, and celebrate collective achievements. Shared responsibility empowers individuals to step outside their comfort zones, take calculated risks, and contribute their unique talents and perspectives to the success of the team.
The Ripple Effect: Accountability Beyond the Team
The impact of a strong culture of accountability extends beyond the immediate team. When individuals feel empowered and accountable for their work, it fosters a sense of professionalism and dedication throughout the organization. This translates to a more efficient workflow, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced brand reputation.
Leading with Accountability: The Road to Success
Ultimately, effective leadership is about inspiring others to achieve extraordinary results. By understanding and fostering a culture of accountability, leaders equip their teams with the ownership and drive to excel. It’s the shift from “just doing their jobs” to actively owning the outcome that unlocks innovation, problem-solving skills, and ultimately, organizational success.
Great leaders take responsibility for their actions and decisions. However, truly effective leaders hold themselves and their teams accountable for achieving exceptional results. It’s this unwavering commitment to accountability that separates good leaders from great ones. By fostering a culture of shared ownership, open communication, and a focus on solutions rather than blame, leaders empower their teams to reach their full potential and drive the organization towards achieving its goals.
Conclusion
The accountability vs responsibility debate highlights the nuanced roles each plays in effective leadership. While responsibility lays the groundwork, accountability serves as the driving force for achieving goals. Leaders who prioritize a culture of accountability unlock a treasure trove of benefits, fostering a team environment where individuals are empowered to take ownership, strive for excellence, and continuously learn from both successes and failures.
Ultimately, effective leadership is about inspiring others to achieve extraordinary results. By fostering a culture of shared accountability, open communication, and a focus on solutions, leaders empower their teams to reach their full potential and drive the organization towards achieving its goals. Remember, great leaders take responsibility for their actions, but truly exceptional leaders hold themselves and their teams accountable for achieving exceptional results. This unwavering commitment to accountability vs responsibility is the defining characteristic that separates good leaders from great ones.
Andrej Fedek is the creator and the one-person owner of two blogs: InterCool Studio and CareersMomentum. As an experienced marketer, he is driven by turning leads into customers with White Hat SEO techniques. Besides being a boss, he is a real team player with a great sense of equality.
