The rise of the gig economy has fundamentally altered the landscape of work. Businesses can now access a vast pool of on-demand talent, while individuals enjoy the freedom and flexibility of project-based work. However, this dynamic environment presents unique challenges for HR compliance. Traditional employee-employer relationships are replaced with looser, more temporary arrangements with gig workers, often classified as independent contractors. This ambiguity can lead to misclassification, confusion over worker rights, and potential legal ramifications.
This article explores the key challenges of HR compliance in the gig economy and proposes solutions to navigate this complex terrain.
Challenges of HR Compliance in the Gig Economy
Classification of Workers
The core challenge lies in accurately classifying gig workers. Misclassifying an employee as an independent contractor can result in significant fines and back-pay obligations for missed benefits like overtime, unemployment insurance, and minimum wage. Determining factors include the level of control exerted by the company, the worker’s independence, and the specialization of the skills required. For instance, a freelance writer with a high degree of autonomy over their work and project deliverables is more likely to be classified as an independent contractor compared to a delivery driver whose route and schedule are dictated by a platform like Uber Eats.
Evolving Legal Landscape
Regulations surrounding the gig economy are constantly evolving. Landmark court cases and legislative changes can redefine the legal status of gig workers, requiring HR teams to stay updated and adjust practices accordingly. This necessitates close collaboration with legal counsel to ensure compliance with local, national, and even international labor laws, especially when working with a geographically dispersed gig workforce. For example, California’s Assembly Bill 5 (AB5) of 2019 established a stricter “ABC” test for classifying workers as independent contractors, impacting companies like Uber and Lyft who heavily rely on gig workers.
Data Privacy and Security
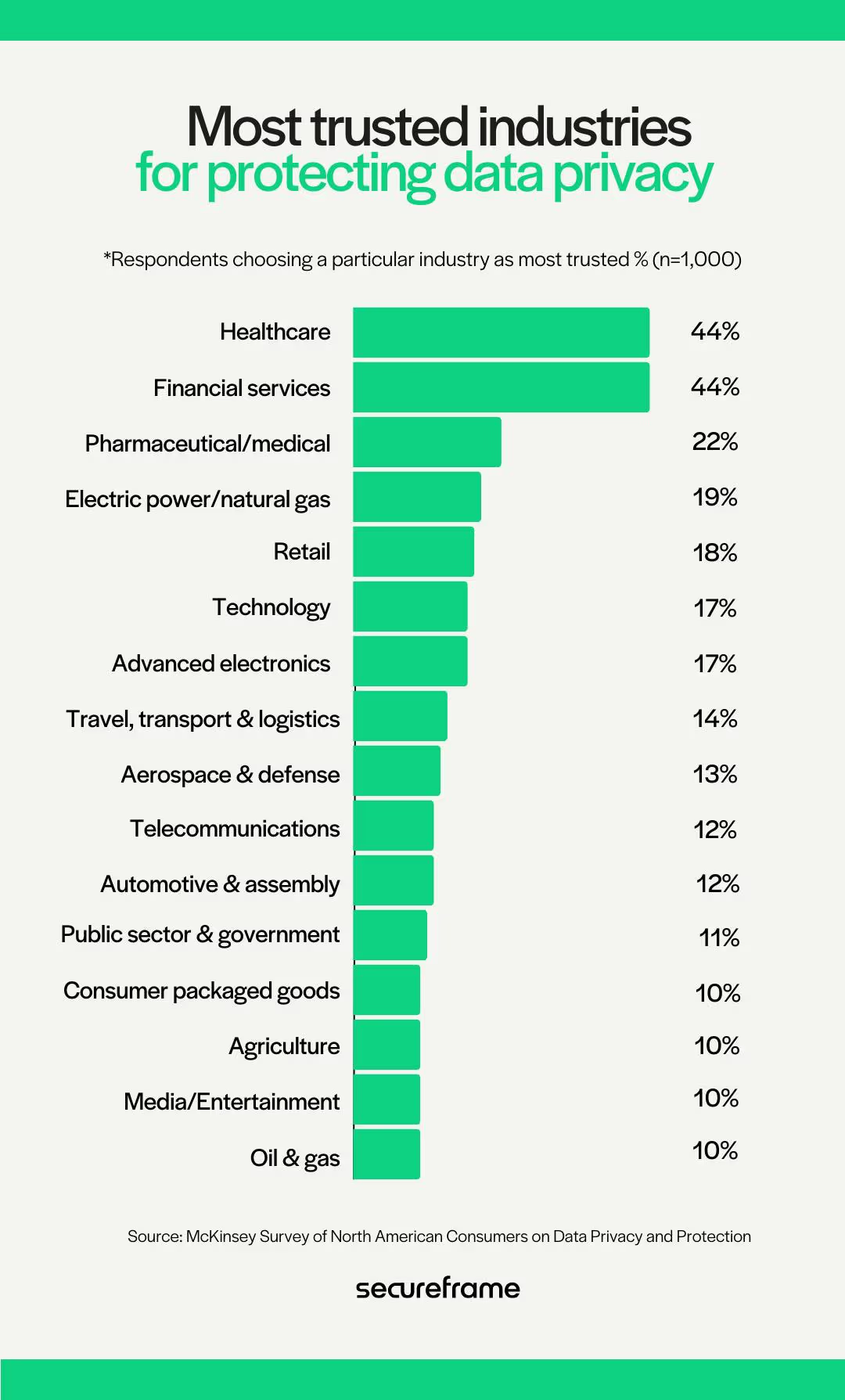
HR departments often collect and store personal data of gig workers, including names, contact information, financial details, and potentially even location data for delivery drivers. Stringent data privacy regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) mandate secure data storage practices and clear communication regarding data usage with gig workers. Failing to comply can lead to hefty fines and reputational damage.
Onboarding and Training
Unlike traditional onboarding processes for employees, gig workers may receive minimal training or orientation. This can lead to safety hazards, non-compliance with company policies, and a disconnect with company culture. For example, a freelance graphic designer working remotely may not be familiar with a company’s brand guidelines or intellectual property policies. Developing effective onboarding programs tailored to the gig workforce is crucial to ensure a safe and productive work environment.
Benefits and Compensation
Gig workers typically receive no benefits or paid time off. While this aligns with the independent contractor model, it raises concerns about worker well-being and potential exploitation. A 2022 study by the Aspen Institute found that 60% of gig workers lack access to health insurance, highlighting the potential financial strain on these individuals. HR teams should explore alternative compensation structures or benefits packages that cater to the specific needs of the gig workforce.
Gig Jobs
- Freelance Writing and Content Creation: Opportunities for writers, editors, and content creators to work with various clients on a project basis.
- Ride-Sharing and Delivery Services: Driving for platforms like Uber, Lyft, or delivering for services such as DoorDash and Uber Eats.
- Web Development and Design: Freelance web developers and designers can find numerous projects to work on, from website creation to app development.
- Virtual Assistance: Offering administrative, technical, or creative assistance to clients remotely.
- Social Media Management: Managing social media profiles and content for businesses and individuals.
- Online Tutoring and Teaching: Educators can provide tutoring services or teach online courses in their area of expertise.
- Graphic Design: Creating visual content for clients, including logos, branding materials, and other designs.
- Translation and Interpretation Services: Offering language translation services for documents, websites, and live interpretation.
- Photography and Videography: Working as a freelance photographer or videographer for events, brands, or media outlets.
- Pet Sitting and Dog Walking: Providing pet care services in your local area.
- Handyman and Cleaning Services: Offering repair, maintenance, or cleaning services through platforms that connect service providers with clients.
- Consulting: Leveraging expertise in a specific field to provide consulting services to businesses and individuals.
- Fitness Training and Wellness Coaching: Providing personal training and wellness advice online or in person.
- E-commerce and Online Retail: Selling products through online marketplaces or personal e-commerce sites.
- Music and Entertainment Gigs: Performing at events, producing music, or offering entertainment services.
Solutions for Effective HR Compliance in the Gig Economy
Clear Contractual Agreements
Well-defined contracts are the cornerstone of a compliant gig worker relationship. These contracts should explicitly outline the nature of the work, compensation terms, ownership of intellectual property, confidentiality obligations, termination clauses, and dispute resolution mechanisms. Ensuring gig workers understand these terms through clear language and readily available translations for a diverse workforce is essential. Additionally, consider including clauses that promote ethical treatment and fair compensation, demonstrating the company’s commitment to a responsible gig economy model.
Independent Contractor Classification Tools
Several online tools and resources can assist HR teams in accurately classifying gig workers. These tools analyze factors such as control, skill set, and integration into the company workflow to determine if the independent contractor classification is appropriate. While these tools offer guidance, it’s crucial to consult with legal counsel for complex situations or geographically specific regulations.
Standardized Onboarding Processes
Developing standardized onboarding procedures for gig workers, even if streamlined, ensures consistency and basic training on company policies, safety protocols, data security measures, and anti-discrimination policies. Onboarding can be delivered online through interactive modules or mobile apps, making it accessible for geographically dispersed workers. Consider incorporating gamified elements or micro-learning modules to enhance engagement and knowledge retention.
Data Management and Security Platforms
Implementing robust data management and security platforms ensures compliance with data privacy regulations. HR teams should adopt practices like data encryption, access control measures with multi-factor authentication, and clear data retention policies that outline how long data is stored and the procedures for secure deletion upon request. Additionally, providing gig workers with transparent information on data collection and usage fosters trust and builds a positive working relationship. Companies can leverage data dashboards to provide gig workers with easy access to their personal information and control over its usage.
Benefits and Compensation Options
While traditional benefits like health insurance and paid time off may not be feasible for all gig workers, HR can explore alternative options to demonstrate a commitment to worker well-being and attract top talent. Here are some possibilities:
Portable Health Insurance Plans
Partnering with insurance providers to offer portable health insurance plans that gig workers can pay into on a voluntary basis can provide much-needed access to healthcare.
Flexible Paid Time Off Policies
Consider offering limited paid time off for specific circumstances like illness or bereavement. This demonstrates compassion and acknowledges the human element of gig work.
Upskilling and Development Opportunities
Providing access to online courses, workshops, or certifications can enhance the skills of gig workers and make them more competitive in the marketplace. This investment can translate into a more skilled and engaged workforce for the company.
Profit-Sharing or Bonus Structures
Tying compensation to project outcomes or performance metrics can incentivize high-quality work and create a sense of partnership between the company and the gig worker.
Technology-Driven HR Solutions

HR technology platforms can streamline the management of a gig workforce. These platforms can automate tasks like:
- Contract Management: Electronic signature capabilities and secure document storage within the platform ensure efficient contract creation, review, and approval processes.
- Worker Classification Assessments: Integration with AI-powered tools can assist with worker classification based on pre-defined criteria and company policies.
- Secure Data Storage: Cloud-based platforms with robust security features ensure data privacy and compliance with regulations.
- Communication and Performance Management: Features like messaging tools, project dashboards, and performance feedback modules can facilitate communication and collaboration between the company and gig workers.
Building a Culture of Compliance
A strong culture of compliance starts from the top. Leadership needs to champion ethical practices and emphasize the importance of fair treatment for gig workers. Regular training for internal teams on HR compliance and worker classification can prevent inadvertent violations. Additionally, establishing clear communication channels for gig workers to report concerns or ask questions fosters trust and encourages responsible practices.
Advantages of Participating in the Gig Economy
Flexibility and Autonomy
Foremost among the attractions of the gig economy is the unparalleled flexibility it offers. Gig workers revel in the ability to control not only their work schedule but also their work location. The freedom to choose when and where one works fosters a healthier work-life balance, a luxury often elusive in more traditional employment setups.
Diverse Income Streams
Diversification becomes a natural consequence of gig work, with many engaged in multiple projects concurrently. This not only provides financial stability by mitigating the impact of any single project’s fluctuations but also opens doors to increased income potential and professional growth. Gig workers can navigate various industries, expanding their skill set and marketability.
Skill Enhancement and Networking
The gig economy provides a unique platform for gig workers to gain exposure to various industries and collaborate with diverse clients. This exposure not only enhances their existing skills but also facilitates the development of a robust professional network. Networking becomes an invaluable asset, often leading to new opportunities and collaborations.
Conclusion
The gig economy presents both opportunities and challenges for HR compliance. By understanding the core challenges, implementing appropriate solutions, and embracing technological advancements, HR teams can navigate this dynamic environment effectively. Building a compliant and ethical gig workforce management system not only mitigates legal risks but also fosters a positive and productive relationship between the organization and its independent contractors.
This approach ensures businesses can leverage the flexibility and talent pool offered by the gig economy while promoting fair treatment and well-being for the individuals who contribute their skills and expertise. By prioritizing compliance and ethical practices, companies can contribute to a sustainable and responsible future for the gig economy.
Andrej Fedek is the creator and the one-person owner of two blogs: InterCool Studio and CareersMomentum. As an experienced marketer, he is driven by turning leads into customers with White Hat SEO techniques. Besides being a boss, he is a real team player with a great sense of equality.
