In the ever-evolving landscape of the modern workforce, the concept of career evolution has become increasingly significant. Gone are the days of linear career paths, where individuals embark on a single trajectory and stay the course until retirement. Today, professionals are faced with a myriad of opportunities and challenges that necessitate constant adaptation and growth. As AI technologies continue to evolve at a rapid pace, they exert a profound influence on the job market, reshaping industries, redefining job roles, and demanding new skill sets from aspiring professionals. This essay endeavors to delve deep into the multifaceted impact of AI on career choices, examining the challenges, opportunities, and ethical considerations that accompany this transformative wave.
Artificial Intelligence, often dubbed as the pinnacle of technological advancement, encompasses a broad spectrum of disciplines, including machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics. At its core, AI seeks to emulate human intelligence processes, enabling machines to learn, reason, and make decisions autonomously. From virtual assistants and chatbots to self-driving cars and sophisticated data analytics tools, AI has permeated various facets of modern life, altering the dynamics of industries and workforce requirements in the process.
Disruption and Transformation of Industries
The advent of AI has sparked a paradigm shift in the traditional landscape of industries, ushering in an era of automation, efficiency, and optimization. In sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and retail, AI-driven automation has revolutionized operational processes, streamlining production lines, optimizing supply chains, and enhancing customer experiences. While these advancements have undoubtedly led to increased productivity and cost savings, they have also precipitated the displacement of certain job roles that were once performed by human workers.
For instance, in the manufacturing sector, AI-powered robots have taken over repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, leading to a decline in demand for manual laborers. Similarly, in the realm of customer service, the proliferation of AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants has redefined the dynamics of client interaction, altering the nature of customer support roles.
Reskilling and Upskilling Imperatives
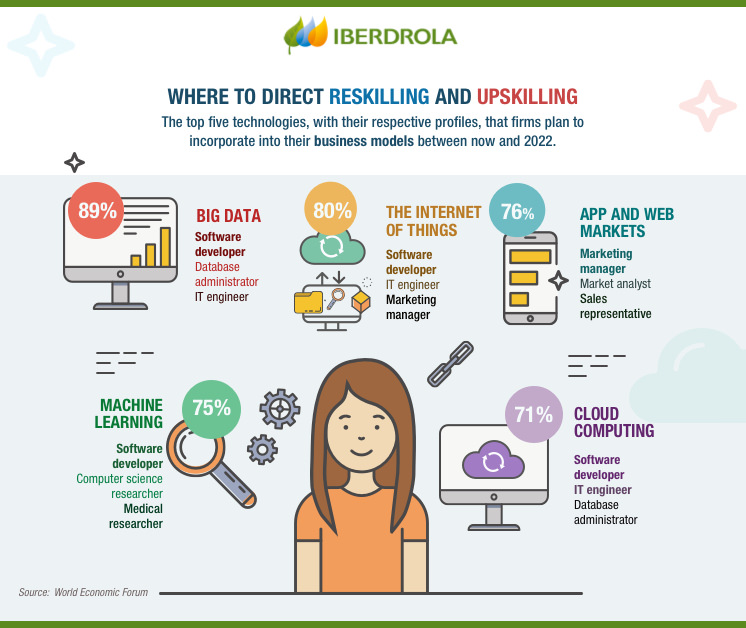
As AI disrupts conventional job roles and automates routine tasks, there arises a pressing need for individuals to adapt and equip themselves with the requisite skill sets to thrive in the AI-driven workforce. The skills demanded by employers are undergoing a significant transformation, with a growing emphasis on technical proficiencies such as data analysis, programming, and AI-specific skill sets. Consequently, individuals are compelled to embark on a journey of continuous learning, reskilling, and upskilling to remain relevant and competitive in the job market.
For example, professionals in the financial services sector are increasingly required to possess data analytics skills to leverage AI algorithms for risk assessment, fraud detection, and investment strategies. Similarly, healthcare professionals are incorporating AI technologies into diagnosis and treatment processes, necessitating proficiency in medical informatics and AI applications in healthcare delivery.
Skill Shifts and Reskilling
The adoption of AI is expected to lead to shifts in the skills required for various jobs, necessitating reskilling and upskilling initiatives for workers to remain competitive in the job market. Workers may need to acquire new skills or undergo retraining to adapt to changing job requirements and technological advancements. Skills that are less susceptible to automation, such as data analysis, statistical modeling, programming, problem-solving, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence, are becoming increasingly valuable in the AI-driven economy. As a result, governments, educational institutions, and businesses are investing in reskilling and upskilling programs to equip workers with the necessary skills to thrive in the evolving job market.
Emergence of New Career Paths
While AI disrupts traditional job roles, it also catalyzes the emergence of novel career paths and opportunities, paving the way for individuals to explore uncharted territories and capitalize on the burgeoning demand for AI expertise. The rapid advancements in AI technology give rise to a plethora of specialized roles, ranging from data scientists and machine learning engineers to AI researchers and robotics specialists.
Moreover, the intersection of AI with various industries spawns interdisciplinary roles that blend AI expertise with domain-specific knowledge, creating a fertile ground for career evolution and professional growth. For instance, the fusion of AI with healthcare gives birth to roles such as medical AI researchers, healthcare data analysts, and AI-powered medical device developers, revolutionizing the landscape of healthcare delivery and patient care.
Entrepreneurial Opportunities
In addition to traditional employment avenues, the proliferation of AI technologies also opens up vast entrepreneurial opportunities for individuals with a penchant for innovation and a entrepreneurial spirit. The democratization of AI tools and resources, coupled with the advent of cloud-based AI platforms and open-source AI libraries, lowers the barriers to entry for aspiring entrepreneurs, enabling them to develop and deploy AI-driven solutions with relative ease and affordability.
From AI-powered startups disrupting traditional industries to innovative ventures leveraging AI for social good, the entrepreneurial landscape is teeming with possibilities for those willing to seize the reins of innovation and harness the transformative power of AI. Whether it’s developing AI-driven apps, launching AI-powered e-commerce platforms, or pioneering AI-based solutions for environmental sustainability, the realm of entrepreneurship offers boundless opportunities for individuals to make their mark in the AI-driven economy.
Ethical and Societal Considerations
In the midst of the whirlwind of AI-driven innovation and disruption, it is crucial to take a moment for contemplation and consider the ethical and societal ramifications of integrating AI into the trajectory of career evolution. The widespread integration of AI into various facets of life raises profound ethical questions regarding accountability, transparency, and fairness in decision-making processes.
One of the foremost ethical concerns associated with AI is the issue of algorithmic bias, wherein AI systems inadvertently perpetuate or exacerbate existing societal biases embedded in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes. From biased hiring algorithms that perpetuate gender or racial biases to AI-driven predictive policing systems that disproportionately target marginalized communities, the specter of algorithmic bias looms large, necessitating robust ethical frameworks and accountability mechanisms to mitigate its adverse effects.
Moreover, the proliferation of AI also raises concerns about the future of work and the potential ramifications of widespread job displacement caused by automation and AI-driven technological advancements. As AI technologies continue to evolve and automate routine tasks, there is a looming threat of job displacement, particularly for individuals in low-skilled and repetitive roles. Consequently, policymakers, industry stakeholders, and educators must collaborate to develop proactive measures to mitigate the adverse effects of job displacement and ensure a smooth transition to the AI-driven workforce of the future.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Job Market
Automation and Job Displacement
AI-driven automation has the potential to impact various industries by replacing tasks traditionally performed by humans. Industries like manufacturing, transportation, retail, and administrative support are particularly vulnerable to job displacement due to the automation of routine and repetitive tasks. For example, in manufacturing, AI-powered robots can perform tasks like assembly and packaging more efficiently than human workers. Similarly, in retail, automated checkout systems and inventory management systems can reduce the need for human intervention. However, the extent of job displacement will depend on several factors, including the pace of AI adoption, the specific tasks involved in various occupations, and the ability of workers to adapt to technological changes. Some jobs may be entirely automated, while others may undergo partial automation, requiring humans to work alongside AI systems. Additionally, new jobs may emerge to support the development, implementation, and maintenance of AI technologies.
Creation of New Jobs
The adoption of AI is expected to create new job opportunities in emerging fields related to AI development, implementation, and maintenance. For example, the demand for data scientists, machine learning engineers, AI researchers, robotics engineers, and software developers with expertise in AI technologies is on the rise. These professionals play a crucial role in designing and implementing AI systems across various industries. Furthermore, as businesses integrate AI into their operations to streamline processes and improve efficiency, there will be a growing demand for workers in roles that complement AI systems. These roles may include AI trainers who teach AI systems how to perform specific tasks, ethicists specializing in AI ethics and regulation, and professionals in human-AI collaboration who ensure effective interaction between humans and AI systems.
Income Inequality
There is concern that the adoption of AI could exacerbate income inequality, as certain individuals and industries may benefit more from AI technologies than others. Workers with skills that are in high demand in the AI-driven economy, such as technical expertise in AI development and implementation, may experience wage growth and increased job opportunities. However, workers in low-skill or routine-based occupations that are easily automatable may face stagnant or declining wages and reduced job prospects. This could widen the gap between high-skilled workers who can leverage AI technologies and low-skilled workers who are displaced by automation, affecting their career evolution. To address income inequality, policymakers may need to implement measures such as progressive taxation, income support programs, and initiatives to promote inclusive economic growth. Additionally, fostering career evolution through reskilling and upskilling programs could help workers transition into roles that are less susceptible to automation.
Job Polarization
Some researchers argue that the impact of AI on the job market could lead to job polarization, where high-skill, high-wage jobs and low-skill, low-wage jobs are in demand, while middle-skill jobs experience a decline. High-skilled jobs that require specialized technical expertise and cognitive abilities, such as data analysis, software development, and AI research, may continue to grow in demand. On the other hand, low-skilled jobs that involve manual labor and routine tasks, such as assembly line work and customer service, may be at risk of automation, leading to a decline in employment opportunities for workers without specialized skills or education. This polarization of the job market could further exacerbate income inequality and socioeconomic disparities, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to support workers in middle-skill occupations
Ethical and Social Implications
The widespread adoption of AI raises ethical and social concerns related to job displacement, algorithmic bias, privacy violations, and the concentration of power in the hands of AI developers and corporations. The use of AI in hiring processes, for example, could perpetuate biases and discrimination if not carefully regulated and monitored. Additionally, there are concerns about the potential for AI systems to replace human decision-making in critical areas such as healthcare, criminal justice, and financial services, raising questions about accountability, transparency, and fairness. Policymakers, businesses, and society as a whole need to address these ethical and social implications to ensure that the benefits of AI are distributed equitably and that workers are protected.
Wrapping up
In conclusion, the impact of Artificial Intelligence on career evolution is a complex tapestry woven with threads of disruption, transformation, and ethical considerations. While AI-driven automation disrupts traditional job roles and necessitates reskilling and upskilling, it also creates a fertile ground for the emergence of new career paths and entrepreneurial opportunities. Amidst the potential of AI-driven innovation, it is essential to proceed with caution, taking into account the ethical and societal consequences of incorporating AI into the process of career evolution.
In essence, career evolution is about taking ownership of one’s professional journey, embracing change, and proactively navigating the challenges and opportunities that arise along the way. By adopting a growth mindset, remaining adaptable, and leveraging technological advancements, individuals can not only survive but thrive in today’s dynamic world of work.
Andrej Fedek is the creator and the one-person owner of two blogs: InterCool Studio and CareersMomentum. As an experienced marketer, he is driven by turning leads into customers with White Hat SEO techniques. Besides being a boss, he is a real team player with a great sense of equality.
